StrategyDriven Portfolio Management Forum

Types of Portfolios
Portfolios are the collections of either assets sharing similar characteristics or activities supporting achievement of common objectives. Individual items with the collection may or may not be interdependent or directly related. These logical groupings, however, facilitate measurement, comparison, and prioritization which in-turn provides portfolio managers with the information necessary to make and implement decisions that maximize value creation for the resources expended.
Management of asset and activity portfolios requires a different focus and skill set. While both asset and activity portfolio management involve the management of resources, asset portfolio management focuses on value creation through the acquisition, deployment, and release of resources whereas activity portfolio management focuses on the prioritization, selection, and execution of value creating work using resources. To better illustrate this concept, the following asset and activity portfolio definitions are offered:
- Asset Portfolios: collections of items the use of which generate value
- Financial: collections of convertible instruments that create value and/or can be exchanged for other resources. Examples include: cash reserves, options, stocks, and bonds
- Material: collections of physical property used in the creation of value adding products and services. Examples include: structures, equipment and tools, and raw materials, components, and supplies
- Intellectual: collections of knowledge resources used in the creation of value adding products and services. Examples include: data, patents, copyrights, trademarks, and retained human knowledge and experience
- Labor: collections of employees, typically grouped by skill set, who perform value adding work. Examples include: managers, engineers, graphic designers, and mechanics
- Activity Portfolios: collections of business activities through which value is created or enhanced.
- Operational Portfolios: collections of the major, ongoing and repetitive activities that either directly or indirectly support organizational value generation. Examples include: marketing, sales, production (of goods and/or services), maintenance, human resources, and finance
- Project Portfolios: collections of projects typically used to enhance or expand existing operational portfolio activities. Examples include: business process reengineering, enterprise resource planning software implementation, and new product/service development
Note: While effective management of both asset and activity portfolios is critical to the success of any organization, postings within the Portfolio Management category will focus on activity portfolios. Insights regarding the management of asset portfolios will be provided within the Resource Management category.
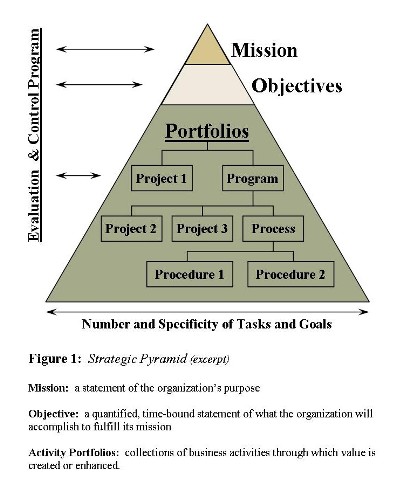
Aligning activity portfolios with the organization’s mission goals necessarily begins with the strategic planning process. Because no one project or recurring activity is likely to satisfy all of an organization’s goals, executives and managers work together to identify, prioritize, and select collections of activities possessing the greatest value potential for a given cost, bounded by the organization’s limited resource availability. Quantifiable measures of value and cost assigned to aid in activity prioritization and selection are then translated into performance measures against which the portfolio manager judges the collection’s ongoing mission alignment. (See Figure 1)
Effective, Efficient Deployment of Resources
Today’s rapidly changing business environment and the dynamic nature of operational activity and project execution demands continuous reevaluation, reprioritization, and, as necessary, redistribution of the organization’s limited resources away from low and no value adding work to those more directly supporting goal achievement. Making resource allocation adjustments to maximize an activity portfolio’s value is, subsequently, a primary responsibility of the portfolio manager.
In order to maximize a portfolio’s ongoing value creation, portfolio managers must act to ensure performance of their portfolio’s activities remains in alignment with and drives achievement of stated mission goals. Therefore, these managers need to clearly understand the organization’s overall objective goals and the value proposition of each activity within their portfolios. It is with this knowledge that they divert resources from low and no value adding work to those more directly supporting goal achievement.
Focus of the Portfolio Management Forum
Materials in the Portfolio Management Forum will focus on the underlying principles, best practices, and warning flags associated with maintaining effective activity portfolio alignment with mission goals while, at the same time, efficiently deploying the organization’s limited resources. The following articles, podcasts, documents, and resources cover those topics critical to a robust portfolio management program.
Articles
Principles
- Managing Shared, Perishable Resources [StrategyDriven Premium Content]
Best Practices
- Best Practice – Identify Interrelationships [StrategyDriven Premium Content]
- Best Practice – The Project Registry [StrategyDriven Premium Content]
- Best Practice – The Project Registry (Continued) [StrategyDriven Premium Content]
Warning Flags
- Warning Flag – Management Distractions [StrategyDriven Premium Content]
StrategyDriven Podcasts
StrategyDriven Podcast – Special Edition


 We have often asserted that organizations, like people, act in a manner consistent with its shared values. Subsequently, those ideals in which an organization’s members truly believe manifest themselves in every aspect of the organization’s physical and social environments. These environments are categorically represented as an organization’s:
We have often asserted that organizations, like people, act in a manner consistent with its shared values. Subsequently, those ideals in which an organization’s members truly believe manifest themselves in every aspect of the organization’s physical and social environments. These environments are categorically represented as an organization’s: Alternative selection is the point in the decision-making process where art meets science and academic knowledge meets hands on experience. There is often no one perfect solution or one best solution. Rather, there will exist several alternatives within the acceptable value range from which the decision-maker will ultimately have to choose one option.
Alternative selection is the point in the decision-making process where art meets science and academic knowledge meets hands on experience. There is often no one perfect solution or one best solution. Rather, there will exist several alternatives within the acceptable value range from which the decision-maker will ultimately have to choose one option.