5 Early Warning Signals for a BPI Project
Can you recognize the early warning signals that derail a business process improvement project? Many articles have been written about what makes process improvement projects fail and usually they list critical success factors. But the real question is how do you recognize the leading indicators in a process? And once you identify those signals what action should you take to cure the ill and get the process back on track or put a halt to the project altogether?
Let’s look at the stages of the BPM Methodology and identify early warning signals and then suggest some countermeasures that are helpful to get things righted again.
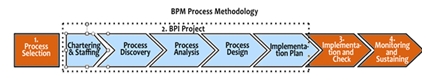
This graphic shows the four stages of the BPM Methodology and the detailed phases of stage 2, the Business Process Improvement Project.
The first early warning signal is in Stage 1, Process Selection, or choosing which process to work on. It’s not that there is one right process to work on first but the choice of a poor project creates many challenges that often lead to a bad name for the whole concept of business process management. The wrong process choice is usually from three circumstances:
- Starting with an enterprise project with several cross-functional stakeholder groups participating.
- Choosing a project where a single Executive Sponsor cannot be designated and it needs two to three Process Owners.
- Starting with a project that requires a different culture than the organization currently has. This would be the case if the culture was authoritarian and it tried to use employee process improvement teams.
The answer to these warning signals is don’t start with a large enterprise process projects without the necessary leaders, and a culture to support it. Instead start smaller, with a key sub process, with leadership and a culture in that function or business unit that support employees working together and understanding how to look at a process and use data, diagrams, and the voice of the customer to improve it.
In the Chartering and Staffing phase of the BPI project there are many critical success factors (It is the beginning of the project! Get it right and you are off to a good start, but get it wrong and you’ll create numerous problem areas). Let me discuss two factors:
The Project Charter
Below are four early warning signals that can come up during the charter process.
- Having no charter. Maybe this happens because the BPM professional staff or IT knows this process needs working on and just begins trying to improve it. There is no written charter, and minimal involvement of the business executives in defining the improvement goals.
- No baseline measures. Without baseline measures, there is no quantitative data to see how critical this problem is, as well as data to see what the current values are and what kind of goal values should be set for the improvement.
- Uncommitted leadership. There is no Process Owner who is designated and steps up to guide this effort, setting the goals, vision, measures, scope, and selecting and providing the necessary team resources. Or the Process Owner has limited time for the team and moves onto other initiatives.
- Overburdened team members. Several team members says they have too many other projects and will not be able to devote time to this additional BPI project.
What can you do in these situations?
- If there is no charter, stop and develop one. Go back and do it. Write it down, put it in the Shared Repository and keep using it and iterating it as the project moves along. If the company has a real anathema to charters, don’t call it a charter, but gather the elements, and name the file something else, or put it in Blueworks Live in the appropriate fields as part of the project overall.
- Once you have the improvement goals for the project they will need measures. So name the appropriate measurement categories and then gather the real baseline data. It doesn’t have to be for the past three years; make it simple. But it may take some manual work this first time because process measures are not automated in most companies today.
- If you have uncommitted leadership, stop. Get different leadership, but make sure they have the responsibility for the process. Or, pick a different process where there is the appropriate Process Owner with commitment to the BPI project. Uncommitted leadership is a big stumbling block –not worth investing in.
- Overburdened team members are usually a sign of a larger problem—the company has too many priorities and keeps adding more assignments without taking some items off the plate. Team members can be ‘conscripted’ to join the team, but if they really do not have time to work on the BPI they will soon start voting with their feet and just not coming to working sessions. So reconsider if this is the right process at this time. Maybe another process where the employees are not so stretched would be better. If just one or two team members are overburdened, it may be possible to find good alternates, but if there are several, don’t start this BPI project.
These are important leading indicators that the process is in trouble. Take the early warning signals as valid information, have a discussion with the appropriate leaders, especially the Process Owner and take action. Otherwise your BPI project could drag on, probably getting weaker, and not moving toward success.
About the Author

, is a highly respected BPM Practitioner. She provides consultation, workshops and training programs for clients ranging from start-ups to Fortune 500 companies, educational institutions, and government organizations. Her programs are based on a unique 3-PEAT method of modeling processes and analyzing data that accelerates operational improvements, and builds leaders and employees who sustain operational excellence. Want to learn more about BPM metrics? Email Shelley at: shelleysweet@i4process.com










Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!